Introduces my research works. The main research areas are: empirical software engineering, software security (software theft detection, software obfuscation), and program education.
:speaking_head: Overview # Recently, to prevent cracking, the various protection methods have been proposed. One of the protection methods is the obfuscation method. Obfuscation method changes the program into hard to understand for hiding secret information in the program.
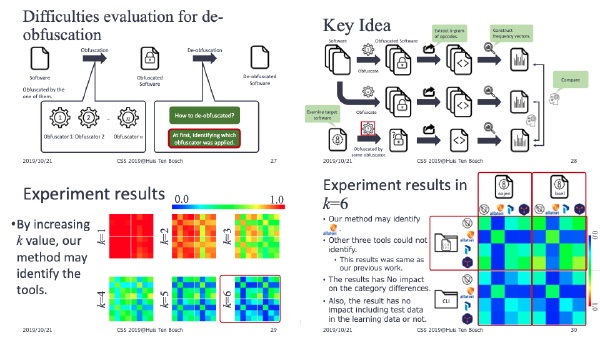
On the other hand, de-obfuscation is an interesting research topic for protecting the software. Since, though vulnerable protection methods are dangerous, measuring the robustness of the method was not discussed.
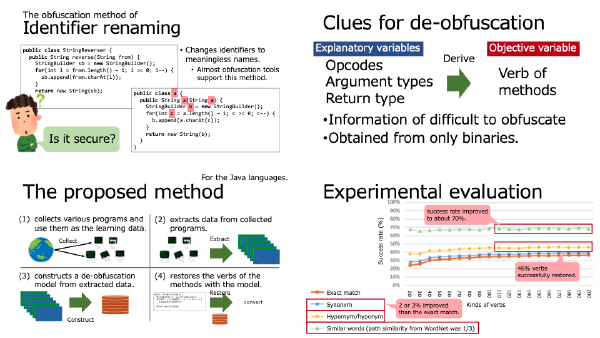
:speaking_head: Overview # The obfuscation methods are often used to hide sensitive information in software. Especially, an identifier renaming method (IRM) is well used because it is easy to implement. IRM is one of the obfuscation methods, and to change the names of function, and variables into meaningless one. However, if we can restore the identifiers to the original names, IRM is invalidated. One of the serious problems about IRM is that the tolerance against de-obfuscation is not discussed. This paper tries to de-obfuscate IRMed programs. Thereby, this paper evaluates the tolerance and effectiveness of IRM. From the experimental evaluation, the proposed method can restore the 49.71 % of method names to the original verbs. Furthermore, focusing on the meanings of verbs, the proposed method recommends the verbs of similar meanings to the original verbs in 57.01 % of methods.
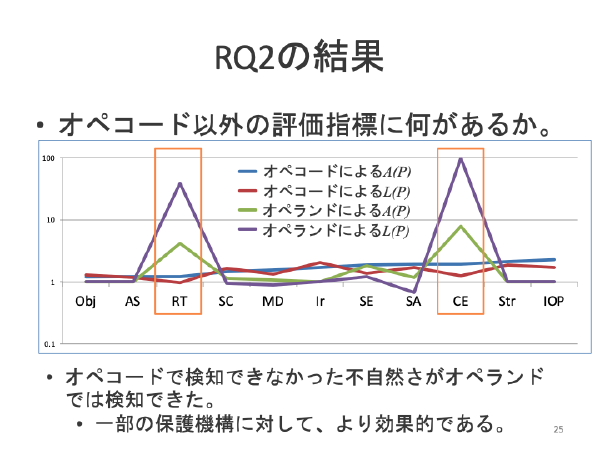
:speaking_head: Overview # This research topic tries to evaluate the artificialities of the obfuscated programs. We believe that the obfuscation changes the programs into unordinal ones. This topics evaluates the artificialities by tf-idf and perplexities.
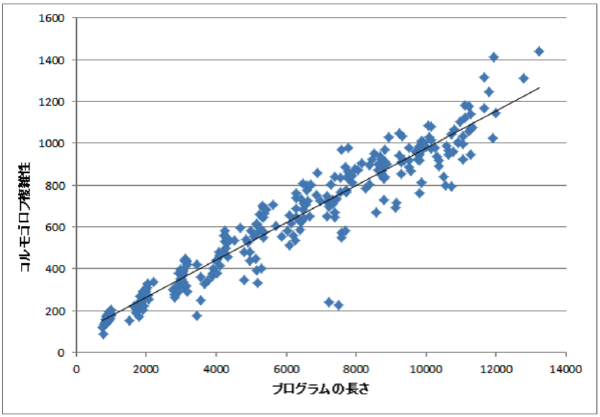
:books: Publications # 横井 昂典,玉田 春昭,”使用クラスに基づいたTF-IDFによる難読化の不自然さ評価”,2017年暗号と情報セキュリティシンポジウム予稿集 (SCIS 2017),3D1-4,January 2017.(沖縄,那覇) 大滝 隆貴,大堂 哲也,玉田 春昭,神崎 雄一郎,門田 暁人,”Javaバイトコード命令のオペコード、オペランドを用いた難読化手法のステルシネス評価”,2014年暗号と情報セキュリティシンポジウム予稿集 (SCIS2014), 2D2-2, January 2014. :mag_right: Related Research Topics # Identifying the applied obfuscator De-obfuscate IRM (identifier renaming method) Evaluating obfuscation method by Kolmogorov complexity Unreadability evaluation of obfuscated programs :handshake: Collaborators # Y. Kanzaki@Kumamoto National College of Technology
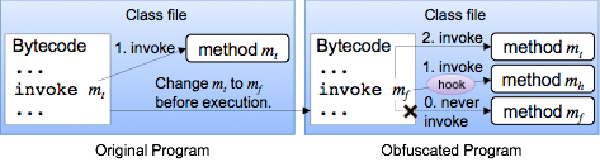
:speaking_head: Overview # This paper proposes an obfuscation method against illegal analysis. The proposed method tries to build a fake call flow graph from debugging tools. The call flow graph represents relations among methods and helps understanding of a program. The fake call flow graph leads misunderstanding of the program. We focus on a hook mechanism of the method call for changing a callee. We conduct two experiments to evaluate the proposed method. First experiment simulates attacks by existing tools: Soot, jad, Procyon, and Krakatau. The Procyon only succeeded decompilation, the others crashed. Second experiment evaluates understandability of the obfuscated program by the hand. Only one subject in the nine subjects answered the correct value. The experiments shows the proposed method has good tolerance against existing tools, and high difficulty of understanding even if the target program is tiny and simple program. (Abstract from IJSI 2015)
:speaking_head: Overview # This paper quantifies the diffuculty of program analysis based on the information theory. The basic idea is to consider that a program ultimately obscated if instructions appear at random; that is (1) all instructions has an equal frequency of appearance, and (2) there is no pattern observed in the instruction sequence. We quantified (1) based on the entropy and (2) based on the Kolmogorov complexity. We evaluated the feasibility of our proposal through a case study.