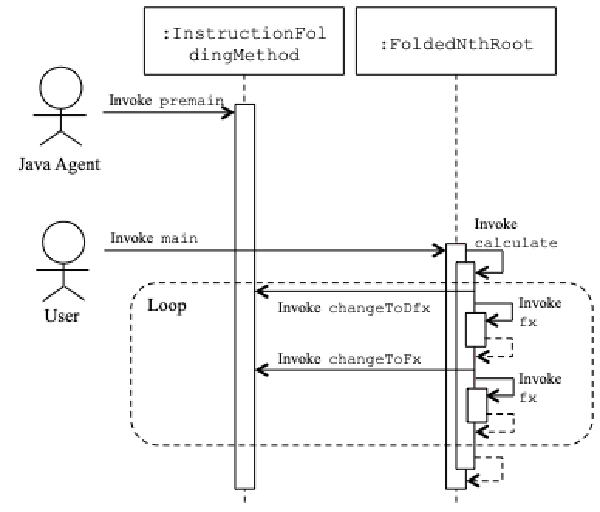
:speaking_head: Overview # To improve tamper resistance of programs against illegal modification, this paper proposes instruction folding applicable to Java platform.
In the proposed method, at first, similar methods are selected in a Java program. Next, these methods are merged into one method and diffs among these methods are stored in the program. Then, at runtime, when one of the merged methods is executed, diffs are restored by self-modification, which is realized by the Java instrumentation mechanism. The proposed method is resilient against tampering of folded method. Even if an adversary modifies the folded method, the program goes crash because the method is repeatedly modified at runtime.
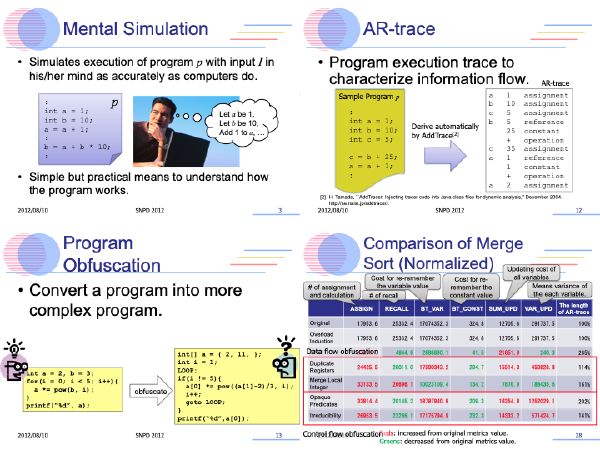
:speaking_head: Overview # Obfuscation methods were proposed for protecting programs from cracking. These methods convert program into incomprehensible one, such as change symbol names from meaningful to meaningless. As a result, secret information in the program can be hidden. However, obfuscation methods are not evaluated sufficiently. This paper evaluates incomprehensibility of the obfuscated programs using queue based virtual mental simulation model (VMSM) which is focused on short term memory in program comprehension. An experimental evaluation showed that VMSM was able to evaluate the incomprehensibility of data and control flow obfuscation methods.
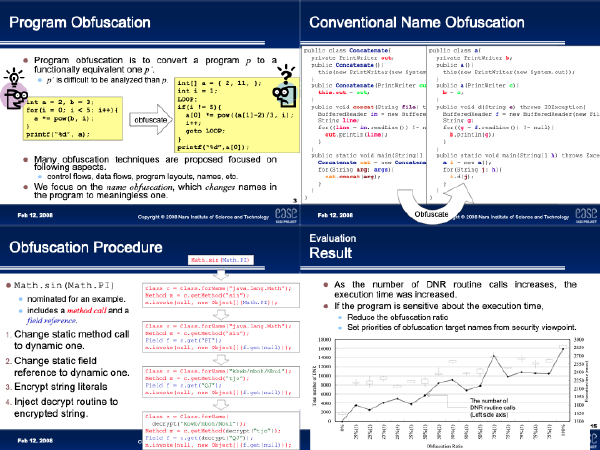
:speaking_head: Overview # Name obfuscation is a software protection technique, which renames identifiers in a given program, to protect the program from illegal cracking. The conventional methods replace names appearing in the declaration part with the meaningless ones. Therefore, the methods cannot be used to obfuscate names declared in system libraries, since changing such system-defined names significantly deteriorates the program portability.